
This selection allows you to eat your fish as sushi or sashimi. Inari Sushi (inari-zushi): is aburage (fried pouches of tofu) stuffed with sushi rice and is sometimes soaked in mirin (sweet sake)Ĭhirashi Sushi (chirashi-zushi): is a bowl of sushi rice topped with a variety of sashimi (raw fish). To show off the skills of the itamae (chef) as it often includes complex layering of Shikaimaki: elegant and very artistic approach of maki sushi that is usually done Uramaki: inside-out rolls, and is a newer style and non-traditional Hosomaki: thin rolls that are usually very simple This roll is usually cut up into 6-8 pieces.įutomaki: thick rolls often due to a lot of ingredients Maki Sushi (maki-zushi or norimaki): is when rice and fish and/or vegetables are rolled up in a seaweed wrap (nori). Temaki Sushi (temaki-zushi): Also called a hand roll and is a cone of sushi rice, fish, and vegetables wrapped in seaweed (nori)
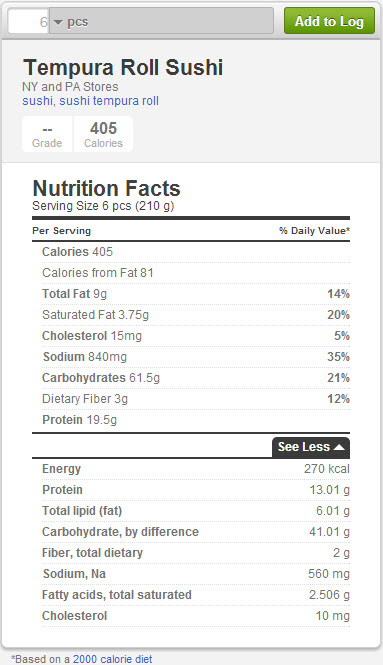
Nigiri Sushi (nigiri-zushi): small oval shaped ball of rice topped with wasabi and a filet of raw or cooked fish or shellfish Sushi Terms to help understand menu options ( ) One sheet of nori will only add about 13 calories to a roll ( ). It is high in protein, many minerals (calcium and iodine), vitamins (A and B12), and fiber. Adding to the nutrition of sushi is nori, which is a dried dark green seaweed used in sushi rolls and wraps. In the West, spicy mayonnaise is a popular addition to sushi rolls (spicy tuna roll) and when seeing the term “tempura” that just means there is fried food (shrimp tempura for example). However, it is prudent to note that extra add-ons can increase the calorie content and fat content considerably. For those needing to watch their carbohydrates such as diabetic or weightlifters, eating sashimi, which is raw fish without the accompaniment of rice would be a valid option. Sushi is generally low in calories, but it is certainly not low in carbohydrates due to the use of rice, and is a good source of high quality protein.

Lactic acid fermentation, accompanied by saccharification of starch by the malted rice, is responsible for the slight sweet-and-sour taste of the product (Koyanagi, T., et al.).

Narezushi is fermented over a longer period than kaburazushi (exceeds 1 month), thus kaburazushi can be recognized as a mid-modern type. By contrast, narezushi is made from salt-(and vinegar-) treated fish and boiled rice is used in place of malted rice. Kaburazushi comprise fillet of salted yellow tail sandwiched between salted turnip, which is piled up in a barrel with malted rice as a fermentor this is fermented for 4-10 days until ready to be consumed. Kaburazushi is a typical medieval sushi introduced to Japanese cuisine sometime during the Edo era (17-19th centuries) and it is still produced and consumed in Ishikawa, Hokuriku region of Japan. Modern Japanese sushi is made from non-fermented vinegar-treated rice and raw fish by contrast traditional sushi production involves fermentation and maturation facilitated by naturally occurring microbes (bacteria).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
